Ever since Satoshi Nakamoto released theBitcoin whitepaper and introduced everyone to the blockchain technology. Ever since then, the blockchain technology seems to have gained a life of its own and has become a subject of interest across a wide variety of companies. Several businesses have started operating with a new business model that is based around the blockchain. In this article, we are going to be talking about successful implementations of blockchain business models.

Traditional Business Models
A business model is a fancy term used to explain the plan/strategy that the company has to generate profit by selling a product or service. The business model provides an outline of the plans of the company to produce a product or service and to market it. Different companies will employ a business model which best suits their needs. There are four traditional business models:
- Manufacturer
- Distributor
- Retailer
- Franchise
Manufacturer

This business model revolves around the creation of the product. The product could either be created from scratch from natural resources or the manufacturer can assemble prefabricated components to make a new product, such as automobiles. A manufacturing business can follow two sub-models. It could either be “business-to-consumer” where they can sell their products directly to the consumers.
Another option involves outsourcing the sales aspect of the process to another company, which is known as the business-to-business or B2B model. In this model, the manufacturers sell their product to the retailers who take care of the sales.
Distributor

The Distributor business model buys the product from the manufacturer and then they either sell it to the end users or a retailer. In a typical supply chain, manufacturers are the point of origin while distributors are the middlemen who connect the manufacturers to their end-users or the retail store.
Retailer

Retailers are brick-and-mortar shops or e-commerce websites which accumulates products from manufacturer either directly or via a distributor. Retailers might be nationwide chains, or they could be independent shops operated by a single entity. Retailers make it extremely easy and straightforward for customers to buy whatever products they want.
Franchise

A franchise business model might involve any of the above-mentioned business models, i.e., manufacturing, distributing, or retailing. Anyone can purchase a franchise which can have both advantages and disadvantages. The main advantage is that a franchise already has all the business processes and protocols integrated inside it. On the flip side, the main disadvantage is the lack of flexibility.
This should give you an idea of the traditional business models that have existed so far. However, ever since the advent of blockchain technology, we have seen a host of new business models. So, before we continue, let’s understand what a blockchain is.
What is the Blockchain?
A blockchain is, in the simplest of terms, a time-stamped series of immutable record of data that is managed by a cluster of computers not owned by any single entity. Each of these blocks of data (i.e. block) are secured and bound to each other using cryptographic principles (i.e. chain).
The three properties of the blockchain technology that is going to help disrupt the supply chain management system are:
- Decentralization
- Immutable
- Transparency
#1 Decentralization
The idea of decentralization is at the very core of blockchain technology. What it means is that any data that is stored inside the blockchain is not owned by one centralized entity but shared by everyone who is part of that blockchain’s network.
#2 Immutability
Immutability means non-tamperable. Any data that you put inside the blockchain cannot be tampered with. Can you imagine how valuable this for modern industries and companies which needs to be constantly on the lookout for cybersecurity? Blockchain attains immutability via cryptographic hash functions.
#3 Transparency
One of the most exciting and misunderstood concepts in blockchain technology is “transparency.” Some people say that blockchain gives you privacy while some say that it is transparent. Why do you think that happens?
Well… a person’s identity is hidden via complex cryptography and represented only by their public address. So, if you were to look up a person’s transaction history, you will not see “Bob sent 1 BTC” instead you will see “1MF1bhsFLkBzzz9vpFYEmvwT2TbyCt7NZJ sent 1 BTC”.
Well… a person’s identity is hidden via complex cryptography and represented only by their public address. So, if you were to look up a person’s transaction history, you will not see “Bob sent 1 BTC” instead you will see “1MF1bhsFLkBzzz9vpFYEmvwT2TbyCt7NZJ sent 1 BTC”.
The following snapshot of Ethereum transactions will show you what we mean:
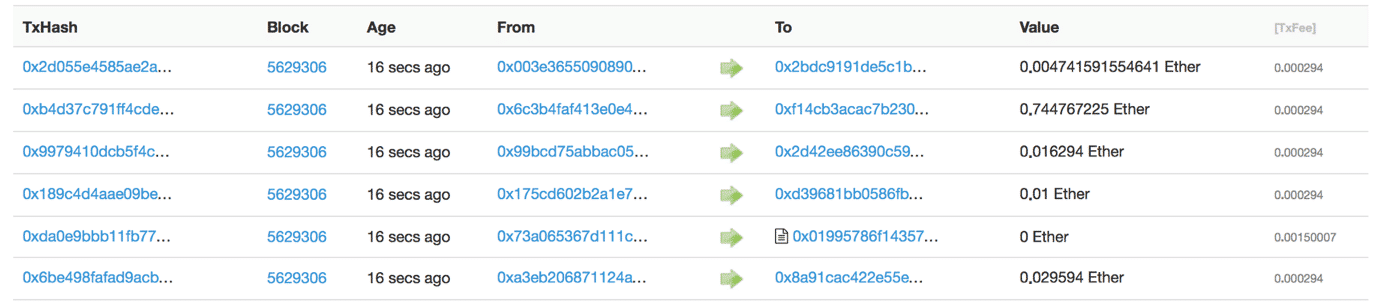
So, while the person’s real identity is secure, you will still see all the transactions that were done by their public address. This level of transparency has never existed before within a financial system. It adds that extra, and much needed, level of accountability which is required by some of these big institutions.
Speaking purely from the point of view of cryptocurrencies, if you know the public address of one of these big companies, you can pop it inside an explorer and look at all the transactions that they have engaged in. This forces them to be honest, something that they have never had to deal with before.
Speaking purely from the point of view of cryptocurrencies, if you know the public address of one of these big companies, you can pop it inside an explorer and look at all the transactions that they have engaged in. This forces them to be honest, something that they have never had to deal with before.
The Need for Blockchain Business Models
With blockchain, organizations can turn their business into decentralization platform which can alter how their business works. It changes the individual elements, the flow of transactions, profits, and also ensures growth. To succeed properly, these models should make sure that they are benefitting both the company’s employees and end users.
Now the question to ask here is, how exactly can one use the blockchain in their business?
- You can store data inside the blockchain which can’t be tampered with.
- Many companies have leveraged the blockchain’s transparency to boost the functionality of their supply chains.
- Many have integrated the blockchain with artificial intelligence to create their own decentralized AI model.
Finally, let’s take a look at some blockchain business models.
Model #1: Utility Token Model

What is the definition of Utility? Utility means the total satisfaction that is received by the consumption of the goods or services. The utility token model drives the functionality in their business via the use of the tokens. Ripple and Stellar are great examples of these kinds of models. The banks who are part of their network can facilitate fund transfer via the use of the XRP or XLM tokens. As per William Mougayar, token utility has three important properties:
- Role
- Features
- Purpose
These three are locked up in a triangle and they look like this:
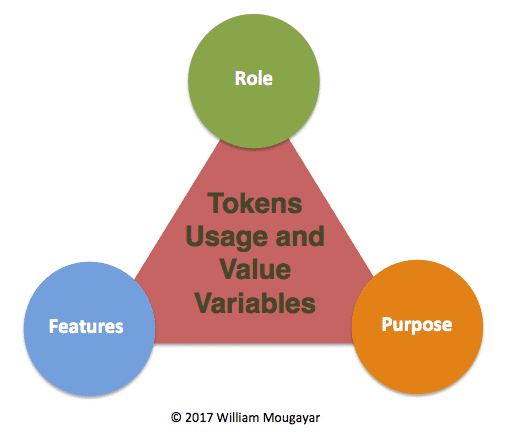
Each token role has its own set of features and purpose which are detailed in the following table:

Let’s examine each of the roles that a token can take up:
- Right: By taking possession of a particular token, the holder gets a certain amount of rights within the ecosystem. Eg. by having DAO coins in your possession, you could have had voting rights inside the DAO to decide which projects get funding and which don’t.
- Value Exchange: The tokens create an internal economic system within the confines of the project itself. The tokens can help the buyers and sellers trade value within the ecosystem. This allows users to gain rewards upon completion of particular tasks. This creation and maintenance of individual, internal economies are one of the most critical functions of tokens.
- Toll: It can also act as a toll gateway for you to use specific functionalities of a particular system. Eg. in Golem, you need to have GNT (golem tokens) to gain access to the benefits of the Golem supercomputer.
- Function: The token can also enable the holders to enrich the user experience inside the confines of the particular environment. Eg. In Brave (a web browser), holders of BAT (tokens used in Brave) will get the rights to enrich customer experience by using their tokens to add advertisements or other attention based services on the Brave platform.
- Currency: Can be used as a store of value which can be used to conduct transactions both inside and outside the given ecosystem.
- Earnings: Helps in an equitable distribution of profits or other related financial benefits among investors in a particular project. Think of staking pools in Cardano.
For this model to effectively the work, the native token must take up as many roles as possible. The more properties the token can tick off, the more utility and value it will bring into the ecosystem
Model #2: Blockchain as a Service
The blockchain and the decentralized ecosystem, in general, can be incredibly intimidating for a newcomer. The Blockchain-as-a-Service (BaaS) model provides a service where a business’ clients can outsource all the scary backend stuff while focussing only on the frontend. BaaS vendors provide services like user authentication, database management, remote updating, and push notifications (for mobile apps), cloud storage, and hosting.
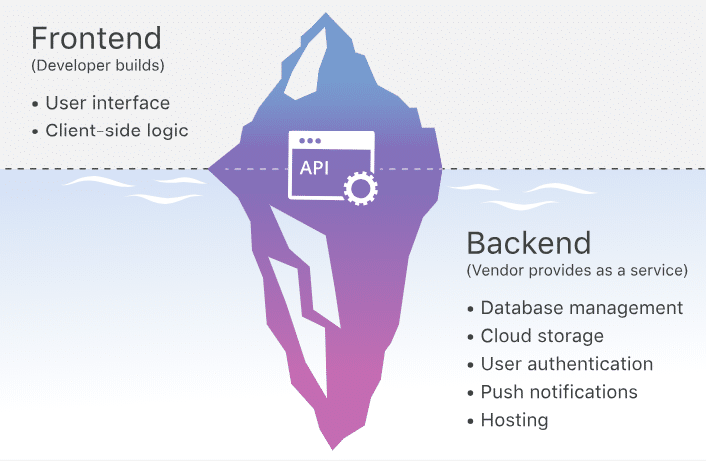
Google Firebase and Microsoft Azure are examples of BaaS providers.
Looking deeper into BaaS

Suppose you have an online business and have created a brilliant website which is bound to get a lot of hits. If you choose to host it from your computer or server, then you will either have to do all the maintenance work yourself (which can be time-consuming) or hire a staff to take of it for you (which can be expensive).
Instead of taking so much stress, you can simply procure the services of an external web hosting provider like Amazon Web Services or HostGator. In exchange for a fee, they will take care of all the infrastructure and maintenance issues.
BaaS works similar to the second option and allows you to focus on your core website functionality. Their service includes support activities like bandwidth management, proper allocation of resources, hosting requirements, and security features like the prevention of hacking attempts.
Importance of BaaS
It won’t be a stretch to call BaaS a necessary catalyst that will lead to broader and deeper penetration of blockchain technology across various industry sectors and businesses. Think about it, an entrepreneur, whose business requires blockchain integration, had only the following options before BaaS:
- Hire blockchain experts. Who are very rare and expensive.
- Train your existing staff on blockchain technology, which is going to take a lot of time and money.
- You can just quit. Now that’s not really going to help anyone.
Even if you somehow still manage to get your blockchain up, you are going to have to deal with all the maintenance. So, why not simply delegate it to the experts?
Many large-scale credible firms have already started offering their BaaS services:
- Microsoft has a BaaS module on its Azure platform.
- IBM has its own BaaS which is focused on private consortium blockchains
- Amazon offers BaaS services.
- Oracle offers blockchain cloud hosting as well.
Model #3: Securities
This is a business model that is a comparatively recent one. Recently, many companies have taken up the securities or “security token offering” business model. A token is classified as security when there is an expectation of profit from the effort of others. If the ICO doesn’t follow specific regulations, then they could be subject to penalties. However, if all the rules are properly met, then these tokens have immensely powerful use-cases.
Since we have already covered utility tokens before, let’s look into the differences between utility and security tokens.
Utility Tokens vs Security Tokens
Alright, so let’s see how these two tokens do head-to-head.
Security Token = Investment Contract
At its very essence, a security token is an investment contract which represents legal ownership of a physical or digital asset like real estate, ETFs, etc. This ownership must be verified within the blockchain.
After the ownership is verified, security token holders can:
- Trade away their tokens for other assets
- Use them as collateral for a loan
- Store them in different wallets
Having said that, the true value in security tokens lies in how they can completely redefine the meaning of “ownership.” They can democratize assets and distribute them among people all over the world. To give a very crude example, instead of owning a gold coin, which may be out of a lot of people’s budget, it is now possible for 100 people to hold fractions of that gold coin.
Model #4: Development Platforms

The blockchain ecosystem is still in its infancy, and the only way it can grow is if more and more developers enter the space. A lot of development and research goes into blockchain as startups are trying to solve problems uniquely. A vast majority of these startups are creating Dapps (decentralized applications) on top of development platforms. So, this begs the question.
Why should developers bother dabbling with the blockchain technology?
- Improves security through decentralization and cryptographic functions.
- Removes immutability via cryptographic hash functions.
- Improves documentation, traceability, and auditability.
- Helps you build an efficient and traceable database.
- Increases trust through transparency.
If you want to know more about the different kinds of blockchain development platforms out there, then you can check out our in-depth guide here.
The Importance of Development Platforms
According to Binance CEO CZ, “For our industry to grow we need more entrepreneurs to build real projects.”
He is not alone in thinking this way. Both Ethereum founder Vitalik Buterin and Tron founder Justin Sun have been encouraging their communities to build real projects on their respective blockchains.
Alright, so some of the smartest people in the blockchain space want there to be more Dapp creation on blockchain platforms. To know the relationship between creating more credible projects on a network and the value of that network itself, we will need to look into the Metcalfe’s Law.
What is Metcalfe’s Law?
Metcalfe’s Law is a theory of network effect. According to Wikipedia, “Metcalfe’s law states the effect of a telecommunications network is proportional to the square of the number of connected users of the system (n^2).”
It was formulated by Bob Metcalfe, the inventor of Ethernet and co-founder of 3Com.
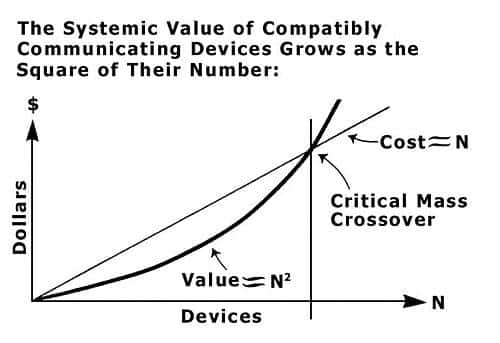
Image Credit: Andrew Chen
Ok so what does this mean and why is this valuable? In simple terms, Metcalfe’s Law states that more the people involved in a network, the more valuable it will be.
Let’s go back to our example of telephones.
If only one person owned a telephone, then it won’t be valuable at all. However, if two or more people own a phone, then it is instantly more valuable since they can now connect and share information.
In fact, we can check this out via the following diagram:
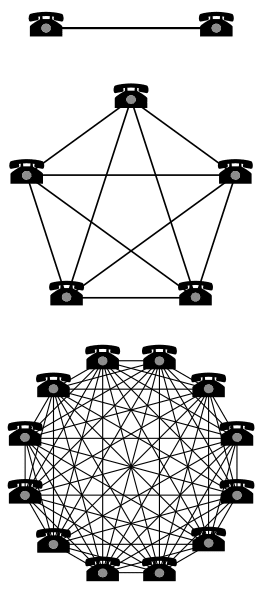
Image Credit: Wikipedia.
As the diagram shows above:
- If you have two telephones in the network, then you can only make one connection.
- If there are 5 phones, then you can make 10 connections.
- However, if there are 12 phones in the network then you can make 66 connections.
That’s a pretty impressive exponential growth!
Plus, one more thing that you shouldn’t forget about networks is that they tend to have a life of their own. Meaning, as more and more people use them, they manage to attract more and more users. This is the reason why most successful networks tend to enjoy extreme exponential growth.
Ok, so we know how vital Dapps are and what they can do to the blockchain ecosystem. However, when it comes to purely business models, how can they bring value into the crypto space? There are three specific models that we want to focus on:
- Network Fees
- Auditing.
- Other Services.
Let’s tackle these one-by-one.
Network Fee
This is a fundamental business model that these development platforms use. Eg. When you create a Dapp on Ethereum, you will need to pay “gas fees” which is like a toll tax that allows you to use the platform. Similarly, in NEO you need to pay for your Dapp with GAS tokens. This is not just applicable to the platforms, even Dapps can charge a nominal network fee. In Golem, you need to have GNT (golem tokens) to gain access to the benefits of the Golem supercomputer. These little nuances help in boosting the strength of the native tokens.
Auditing
Smart contract auditing is one of the more critical services that one can provide within the ecosystem. Since these Dapps deal with a lot of money, it is imperative for their code to work correctly. Any slight error or bug can lead to a complete catastrophe. Eg. A simple bug in the DAO smart contract caused Ethereum’s community to split up into Ethereum and Ethereum Classic. There are two ways that this model can work:
- The developers hire an auditing company to look over the smart contract for them.
- The developers put up a bounty on their contract and several independent auditors and developers can look up the code and search for flaws.
Other Services
A blockchain startup requires a ton of work. They need a good website, good content, good frameworks, etc. To save up on time and money, these startups either hire freelancers or agencies to take care of these services for them.
Conclusion
So, there you have it. These are the business models currently present in blockchain-based companies. Have we missed out on some models? If yes then let us know in the comments below.
Copied from: https://blockgeeks.com/guides/understand-blockchain-business-models/




No comments:
Post a Comment